Steps in preparation of site for construction works involves geotechnical report, site clearing, excavation, grading and compaction. Steps for construction site preparation are discussed.
Preparing Site for Construction Projects
To construct excellent project, the condition of the project site including subsurface and surface condition must be investigated and assessed thoroughly.
Site assessment may involve determining the present and installation of underground services, specify suitable foundation depend on recommendation of geotechnical report, anticipate the level of ground water, grading amount needed for proper drainage to push water away from the structure, whether the site is difficult to excavate or not, frost penetration depth.
To build the structure as per the design, estimate the excavation volume accurately, and provide suitable drainage, structural elevations and layout must be carried out with substantial precision.
Steps in Preparing Site for Construction Projects
Stages or steps which are needed to undertake to prepare the construction project site are.
- Geotechnical report related to site soil properties
- Construction site clearing and excavation
- Grading of project site
- Project site compaction
Geotechnical Report related to Site Soil Properties
Geotechnical report creates communication between project site condition and design and construction recommendation. Therefore, to understand properties and condition of the soil of the project site, a geotechnical report about the soil of the site is a must.
This report commonly describes soil property and provides necessary recommendation. It is produced based on a series of tests on soil. Type of the structure dictates sampling method, type of test, and number of test required.
After achieving and interpreting test results, type of foundation appropriate for the site, settlements and related recommendations, liquefaction possibilities, slope stability, groundwater level, soil bearing capacity, excavation related hazards, soil strength, soil classification, and many more information are provided in the geotechnical reports.
These invaluable data adequately define the properties of soil and its behavior in the future. If the project site prone to earthquake, then necessary testing and recommendation should be included in the geotechnical report.
Fig.1: Preparing Site for Construction Projects

Fig.2: Borehole Sampling for Geotechnical Report
Construction Site Clearing and Excavation
Clearing and excavation is part of the greater job which is carried out in preparing site for construction projects. As shown in Figure-3, trees and all sorts of vegetation on the site are removed at site clearing phase.
After the layout of the structure is set accurately, the excavation work begins and the soil is removed to a required depth in which the foundation of the structure is placed.
There are various types of machinery used to excavate and transport soil at project site. The selection of the type of machinery employed for excavation is based on the soil type, how long is the distance the soil need to be transported, soil site ability to carry load, and site accessibility.
For instance, blasting, drilling, and machinery like boulders, backhoe, shovels, and scooper are involved to excavate and transported blasted and drilled materials when rocks are present at the site.

Fig.3: Clearing Construction Site

Fig.4: Removing Excessive Soil and other Materials from Construction site

Fig.5: Construction Site Excavation
Grading of Construction Project Site
Grading at constructed site is very crucial to force water away from the structure. International Building Code (IBC 2009), provides necessary recommendation to create proper grading.
The Code states that grade slope should be at least one unit vertical to twenty units horizontal in other words 5% at a distance of 3m measured perpendicular from the wall face.
If a horizontal distance of 3 m is not available due to physical hinders, then other options need to be employed such as swales and impervious surface for which least slope should be 2% if is located within the limit of 3m. The IBC code permit minimum slope of one unit horizontal to forty-eight-unit vertical under certain conditions.
If the construction site is not flat, then suitable cutting and filling need to be carried out and the both cut and fill volume is dictated by the lowest level placement of the structure.
Final settlement of soil should be considered while grading is carried out.
Compaction of Construction Project Site
Soil beneath foundation at site construction must be compacted to the required degree which as per IBC Code is 90% of maximum dry density. Compaction of soil layers which support loads is a must because it decreases settlement and consequently prevents undesired incidents.
Tamping, rolling, and vibration are types of loads employed to compact soil layers. there are several machines used for compaction at construction site such as smooth wheel roller, sheep foot roller, rubber tire, crawler, and tamping plate compactor.
Not only does the compaction of soil improve shear strength but also it declines soil permeability and compressibility.
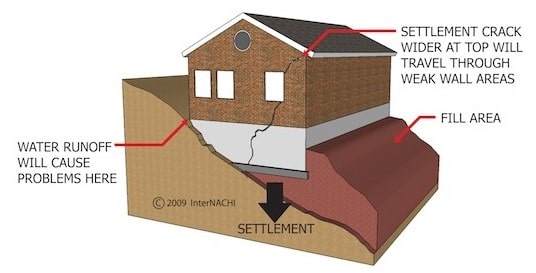
Fig.6: Bad Compaction and Poor Grading led to Cracks in the Building

Fig.7: Standard Proctor Test for Soil Compaction
Optimum moisture content should be provided to obtain target degree of compaction. In this regard, silt and clay are considerably sensitive because improper moisture content lead to fail the process and poor compaction will be achieved which usually is not desirable.
The optimum moisture content and compaction percentage are determined by either standard modified or proctor modified compaction test in laboratory.
Source: theconstructo excluding headline



